What is decentralised finance?
Decentralised finance (DeFi) is a nascent financial system that relies on secure distributed ledgers, such as the ones used by cryptocurrencies.
In the United States, the Federal Reserve and Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) establish regulations for centralised financial institutions such as banks and brokerages. Consumers rely on these institutions to directly access money and financial services. DeFi disrupts the centralised financial system by enabling people to engage in peer-to-peer transactions.
How Decentralised Finance (DeFi) Works
DeFi utilises security protocols, connectivity, software, and hardware developments within peer-to-peer financial networks. This solution obviates middlemen such as banks and other financial service businesses. These corporations impose fees on businesses and users for using their services, which are essential under the present system since they are the only means to ensure its functionality. DeFi leverages blockchain technology to minimise its reliance on middlemen.
Blockchain
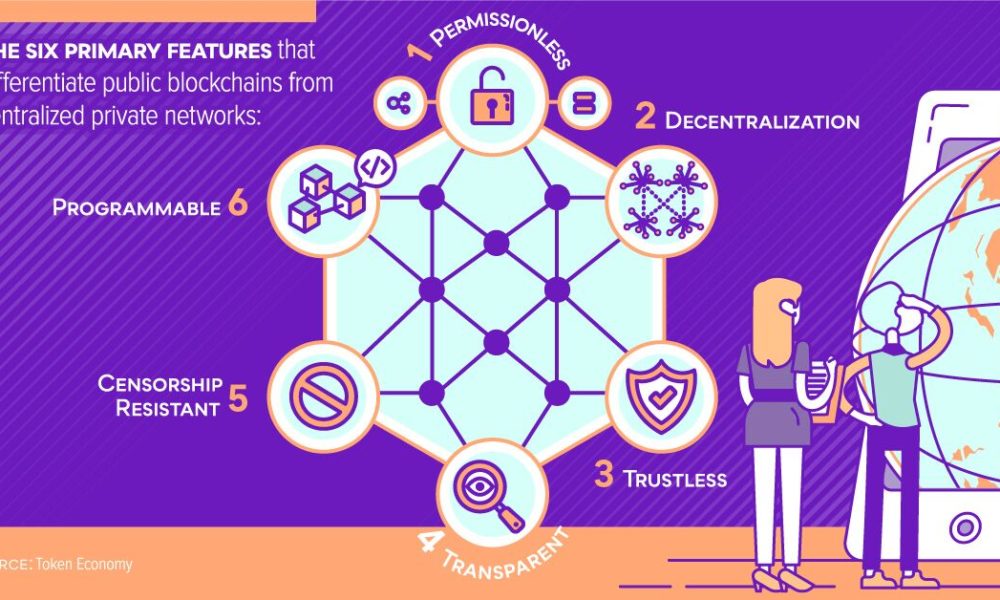
A blockchain is a decentralised and encrypted database or ledger. Transactions in the blockchain are documented in blocks and authenticated using automated procedures. Once a transaction is validated, the block is sealed and encrypted. Subsequently, a new block is generated, including details of the previous block as well as information about more recent transactions.
The term “blockchain” refers to how the information in each subsequent block connects the previous blocks. Modifying data in prior blocks of a blockchain would have a cascading effect on subsequent blocks, making it impossible to modify the blockchain. The inclusion of additional security procedures in addition to this notion ensures the inherent security of a blockchain.
Individuals use wallet software to securely store private keys, which serve as passwords, and may transmit data to a blockchain network. These private keys provide access to tokens or cryptocurrencies. These keys provide them with access to digital tokens that symbolise value. By “transmitting” a specific number of tokens to another entity through a wallet, which then generates a unique private key for them, ownership of the tokens can change. By securing their possession of the token, and due to the blockchain architecture, the transfer has become irreversible.
Applications
DeFi apps are specifically intended to establish direct communication with a blockchain, enabling individuals to use their funds for various purposes like purchases, loans, presents, trading, or any other desired transactions, all without the involvement of intermediaries. These apps are software programmes that are loaded on devices such as personal computers, tablets, or smartphones to enhance usability. In the absence of apps, DeFi would continue to exist, but users would be required to possess a certain level of comfort and familiarity with using the command line or terminal on their device’s operating system.
DeFi programmes provide a user-friendly platform that automates transactions between users, providing them with a range of financial choices. For instance, if you want to lend money to someone and impose interest on them, you may choose the corresponding option on the interface and input parameters such as interest or collateral. If you need a loan, you have the option to explore several sources, which may include traditional financial institutions such as banks or even individuals who are willing to lend you bitcoin, subject to mutually agreed-upon conditions.
Certain programmes allow users to input specific specifications for the desired services and then pair them with another user who meets those criteria. Due to the decentralised nature of the blockchain, individuals have the ability to engage in financial transactions from any location worldwide.
Very Important: Decentralised money does not provide complete anonymity. Transactions are anonymous but may be traced by someone with the necessary expertise. This include governmental bodies and law enforcement agencies, which are sometimes crucial in safeguarding an individual’s financial concerns.
Goals of Decentralised Finance
Peer-to-peer (P2P) financial transactions are a fundamental concept in DeFi, where two people mutually agree to trade bitcoin for products or services without the involvement of a third party.
Utilising decentralised finance (DeFi) enables the following:
Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection can access a DeFi platform, and transactions can take place without any restrictions based on location.
DeFi facilitates direct negotiation of interest rates between two parties, allowing them to lend cryptocurrency or money via DeFi networks with low costs and high interest rates.
Security and transparency are ensured via the use of smart contracts recorded on a blockchain. These contracts, together with records of completed transactions, are accessible for anyone to examine. However, they do not disclose your name. Blockchains are inherently immutable, which signifies that they are incapable of being altered or modified.
Autonomy: DeFi platforms operate independently without depending on centralised financial institutions. The decentralised structure of DeFi protocols reduces the need for and expenses associated with managing financial services.
Fact Check: Peer-to-peer lending within the context of decentralised finance (DeFi) does not imply the absence of interest and fees. Nevertheless, this implies that you will have a plethora of choices since the lender might be located anyplace globally.
Disadvantages of DeFi
Decentralised finance is in a perpetual state of evolution. The system lacks regulation, making it susceptible to programming errors, hacking, and fraudulent activities. One of the primary methods by which hackers and criminals pilfer cryptocurrency is by exploiting vulnerabilities in DeFi programmes.
Legislation has not yet kept pace with the rapid progress in technology. The majority of existing laws were formulated on the premise of distinct financial jurisdictions, each with its own set of laws and regulations. The borderless transaction capability of DeFi raises crucial inquiries about its regulation. As an illustration:
The responsibility for investigating a financial crime that spans across borders, protocols, and decentralised finance (DeFi) applications lies with the appropriate authorities or law enforcement agencies.
Which entity would be responsible for enforcing the regulations?
What methods would they use to ensure compliance with the rules?
What does decentralised finance do?
The objective of DeFi is to disrupt the reliance on centralised financial institutions and intermediaries in all financial transactions.
Does Bitcoin belong to the realm of decentralised finance?
Bitcoin is digital money. DeFi is specifically built to use cryptocurrency inside its ecosystem; hence, Bitcoin may be considered a component of DeFi rather than being synonymous with it.
What is the definition of total value locked (TVL) in the context of decentralised finance (DeFi)?
Total value locked (TVL) is the aggregate value of all cryptocurrencies that have been staked, borrowed, put in a pool, or used for other financial activities inside the decentralised finance (DeFi) ecosystem. Additionally, it might denote the aggregate value of certain digital currencies used for financial transactions, such as ether or bitcoin.
Summary
Decentralised finance (DeFi) is a nascent financial technology that poses a threat to the existing centralised banking system. DeFi aims to eliminate the fees imposed by banks and other financial service providers while encouraging direct transactions between individuals.
DeFi, like the blockchains and cryptocurrencies it sustains, is now in its early stages of development. Before it can replace the current financial system, which itself has intractable problems, there are substantial obstacles that must be surmounted. Financial service organisations and banks will fiercely resist being replaced, and if there is an opportunity for them to benefit from the shift to a blockchain-based financial system, they will actively seek it out and ensure their involvement.
Leave a Reply